Everything You Need to Know About FDM 3D Printers
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of manufacturing and design, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers have carved out a significant niche. These versatile machines have revolutionized how we create everything from prototypes to finished products. But what exactly are FDM 3D printers, and how do they work? Let’s dive into the world of FDM technology and explore why it has become a game-changer in the manufacturing industry.
What Are FDM 3D Printers?
FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a popular additive manufacturing technology. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that often involve subtracting material from a larger piece, FDM builds objects layer by layer. This process is akin to constructing a complex model out of LEGO bricks, one piece at a time, until the entire structure is complete.
How Do FDM 3D Printers Work?
The magic of FDM printing lies in its simplicity and precision. Here’s a breakdown of how these printers operate:
Design Creation: The journey begins with a 3D digital model, typically created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software.
Slicing the Model: The 3D model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using specialized software.
Printing Process: The printer’s nozzle heats up the filament (usually thermoplastic) and extrudes it layer by layer, following the sliced design.
Layer Bonding: Each new layer bonds to the previous one, creating a solid object.
Final Touches: Once printing is complete, the object may require some post-processing, like removing support structures or smoothing surfaces.
Mecolour new arrival ME-O22F 3D printer
Benefits of FDM 3D Printers
Why are FDM 3D printers so popular? Here are some of the key advantages:
Cost-Effective
FDM 3D printers are relatively affordable compared to other types of 3D printers. The materials used, mainly thermoplastics like PLA and ABS, are also inexpensive. This makes FDM a cost-effective solution for both hobbyists and professionals.
Versatility
These printers can produce a wide variety of objects, from simple prototypes to intricate designs. The ability to use different materials, including those with various colors and properties, adds to their versatility.
Ease of Use
FDM printers are user-friendly, making them accessible even to beginners. With straightforward software and minimal setup requirements, you can start printing your designs in no time.
Quick Turnaround
With FDM technology, you can quickly transform digital models into physical objects. This rapid prototyping capability is invaluable in industries where time is of the essence.
Applications of FDM 3D Printers
FDM 3D printers aren’t just for hobbyists tinkering in their garages. They have a wide range of applications across various industries.
Prototyping
One of the primary uses of FDM printers is rapid prototyping. Engineers and designers can create functional prototypes quickly and cost-effectively, allowing for iterative testing and refinement before mass production.
Manufacturing
In some cases, FDM printers are used for manufacturing small batches of parts. This is especially useful for custom or low-volume production runs where traditional manufacturing would be too expensive.
Education
Schools and universities use FDM printers to teach students about engineering, design, and manufacturing. These hands-on tools bring lessons to life and inspire innovation.
Medical Field
The medical industry leverages FDM printing for creating custom prosthetics, surgical guides, and even models for surgical planning. The ability to tailor-make solutions is a significant advantage.

Applications of FDM 3D Printers
Choosing the Right FDM 3D Printer
When selecting an FDM 3D printer, consider the following factors to ensure you get the best fit for your needs:
Print Volume
The print volume determines the maximum size of the objects you can create. If you plan to print large items, look for a printer with a larger build area.
Resolution
Resolution refers to the layer height and the level of detail the printer can achieve. Higher resolution means finer details, which is crucial for intricate designs.
Filament Compatibility
Ensure the printer is compatible with the types of filament you intend to use. Some printers are limited to specific materials, while others offer more flexibility.
Ease of Maintenance
Look for printers that are easy to maintain and have readily available parts. This will save you time and money in the long run.
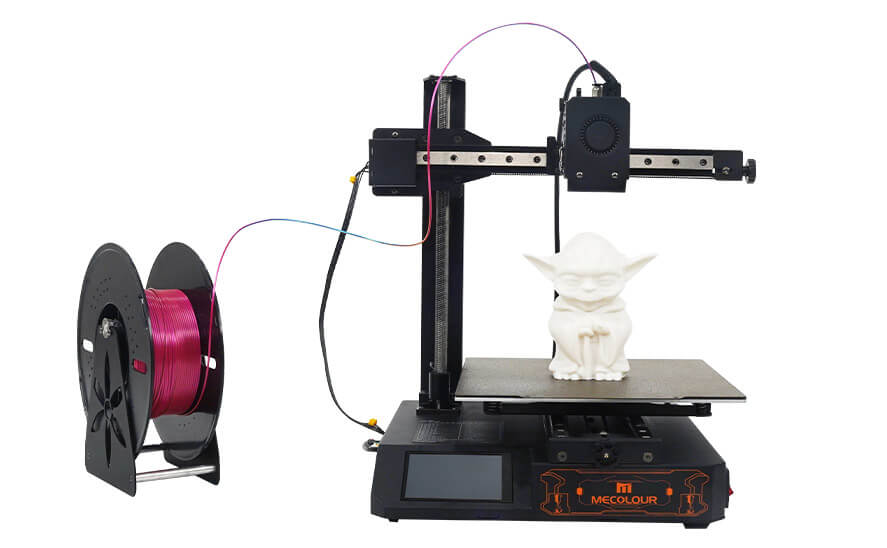

mecolour 3d printer
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even the best FDM 3D printers can encounter problems. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
Warping
Warping occurs when the edges of a print curl up, causing distortion. This can be mitigated by using a heated bed and ensuring proper adhesion of the first layer.
Stringing
Stringing happens when small strands of filament appear between parts of the print. Reducing the printing temperature and adjusting retraction settings can help.
Layer Shifting
Layer shifting occurs when layers are misaligned. This can be due to loose belts or issues with the stepper motors. Tightening the belts and checking motor connections usually resolve this problem.
Inconsistent Extrusion
If the filament is not extruding consistently, it could be due to a clogged nozzle or issues with the extruder gear. Cleaning the nozzle and ensuring the filament is feeding smoothly can fix this.
The Future of FDM Technology
FDM 3D printing is continuously evolving. With advancements in materials, software, and printer technology, the future looks bright. Here are some trends to watch:
New Materials
Researchers are developing new filaments with enhanced properties, such as higher strength, flexibility, and conductivity. These materials will expand the range of applications for FDM printers.
Improved Software
Software improvements are making slicing more efficient and user-friendly. Enhanced algorithms can optimize print paths, reducing print times and improving quality.
Multi-Material Printing
Future FDM printers may be capable of printing with multiple materials simultaneously. This could allow for complex objects with varying properties within a single print.
Accessibility and Affordability
As technology advances, FDM printers are becoming more affordable and accessible. This democratization of 3D printing technology will open up new possibilities for creators worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FDM 3D printers are powerful tools that have revolutionized the way we design and manufacture products. From rapid prototyping to custom manufacturing, their versatility and affordability make them an attractive option for a wide range of applications. By understanding the basics of how FDM printers work, their benefits, and how to choose the right one, you can unlock a world of possibilities and take your creations to the next level.





